1. What is the <title> Tag
The HTML Page Title is defined by the <title> tag, displayed in the browser tab, search results, and bookmarks. It’s vital for SEO, user experience, and accessibility—keep it concise, descriptive, and unique for each page.
The <title> tag is an HTML element used to define the title of a web page. This title is displayed in:
- The browser’s title bar or tab.
- Search engine results (as the clickable headline for the page).
- Bookmarks or favorites when a user saves the page.
It is a required element in every HTML document and must be placed within the <head> section.
Syntax
<title>Your Page Title Here</title>- The
<title>tag is a container tag, meaning it has an opening (<title>) and closing (</title>) tag. - The text between the opening and closing tags is the title of the page.
2. Where to Place the <title> Tag
The <title> tag must be placed inside the <head> section of the HTML document. The <head> section contains metadata (information about the document) that is not displayed on the web page itself.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Awesome Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1>
<p>This is a sample HTML page.</p>
</body>
</html>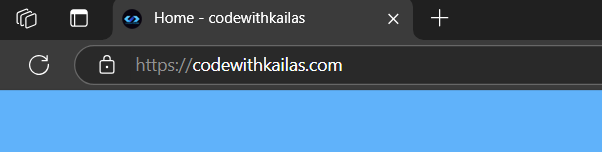
3. Key Features of the <title> Tag
Browser Display:
- The title appears in the browser’s title bar or tab.
- Example: If the title is “My Awesome Web Page,” the browser tab will display this text.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
- Search engines like Google use the
<title>tag to understand the content of the page. - A well-written title can improve the page’s ranking in search results.
Bookmarks:
- When a user bookmarks the page, the title is used as the default name for the bookmark.
Accessibility:
- Screen readers use the title to announce the page to visually impaired users.
4. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Missing <title> Tag:
- Without a
<title>tag, the browser will display the file name or a blank title, which looks unprofessional.
Using the Same Title for All Pages:
- This can confuse users and search engines, making it harder to distinguish between pages.
Writing Titles That Are Too Long:
- Long titles may get cut off in search results or browser tabs.
Ignoring SEO:
- Failing to include relevant keywords can make it harder for your page to rank in search results.
5. Browser Behavior
- If you don’t include a
<title>tag, the browser will display the file name or a blank title. - Example: If the file is named
index.html, the browser tab might display “index.html” instead of a proper title.
Conclusion
The <title> tag is a small but crucial part of an HTML document. It plays a significant role in:
- Improving user experience by clearly identifying the page.
- Enhancing SEO by helping search engines understand and rank the page.
- Ensuring accessibility for screen reader users.
