The HTML id Attribute is one of the most fundamental and widely used attributes. It is used to uniquely identify an element within an HTML document. This guide will explain everything about the id attribute, from its basic usage to advanced applications, best practices, and common pitfalls.
1. What is the HTML id Attribute
The id attribute is a global attribute in HTML, meaning it can be applied to any HTML element. Its primary purpose is to provide a unique identifier for an element. No two elements in the same document can have the same id value.
Key Characteristics:
- Uniqueness: Each
idvalue must be unique within the document. - Case Sensitivity: The
idattribute is case-sensitive (e.g.,headerandHeaderare considered different). - Global Use: It can be applied to any HTML element, such as
<div>,<p>,<span>,<input>, etc.
2. Syntax of the id Attribute
The id attribute is added to an HTML element as follows:
<element id="unique-id">Content</element>element: Any HTML element (e.g.,<div>,<p>,<h1>, etc.).unique-id: A unique identifier for the element. It must start with a letter (A-Z or a-z) and can be followed by letters, digits (0-9), hyphens (-), underscores (_), colons (:), or periods (.).
3. Why Use the id Attribute
The id attribute is used for several purposes:
a. Styling with CSS
You can use the id attribute to apply specific styles to an element using CSS. In CSS, the id selector is prefixed with a hash (#).
Example:
<style>
#header {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
</style>
<div id="header">Welcome to My Website</div>b. JavaScript Manipulation
The id attribute is commonly used to access and manipulate elements using JavaScript. The document.getElementById() method is used to select an element by its id.
Example:
<script>
document.getElementById('header').innerHTML = 'New Header Text';
</script>c. Anchor Links
The id attribute can be used to create anchor links within a page. This allows users to navigate to a specific section of the page.
Example:
<a href="#section1">Go to Section 1</a>
<div id="section1">
<h2>Section 1</h2>
<p>This is the content of Section 1.</p>
</div>d. Form Label Association
The id attribute is used to associate a <label> element with a form control (e.g., <input>, <textarea>). This improves accessibility and usability.
Example:
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username">4. Rules for Using the id Attribute
- Unique Value: Each
idvalue must be unique within the document. Duplicateidvalues are invalid and can cause issues in CSS and JavaScript. - Case Sensitivity: The
idattribute is case-sensitive. For example,headerandHeaderare considered different. - Valid Characters: The
idvalue must begin with a letter (A-Z or a-z) and can be followed by letters, digits (0-9), hyphens (-), underscores (_), colons (:), or periods (.). - No Spaces: Spaces are not allowed in
idvalues.
5. Practical Examples
Example 1: Basic Usage
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>ID Attribute Example</title>
<style>
#header {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
#content {
background-color: lightgray;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="header">Welcome to My Website</div>
<div id="content">
<p>This is the main content of the page.</p>
</div>
<a href="#header">Back to Top</a>
</body>
</html>Example 2: JavaScript Interaction
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JavaScript and ID Example</title>
<script>
function changeText() {
document.getElementById('demo').innerHTML = 'Text Changed!';
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="demo">This is a paragraph.</p>
<button onclick="changeText()">Change Text</button>
</body>
</html>Example 3: Form Label Association
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Form Label Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username"><br><br>
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>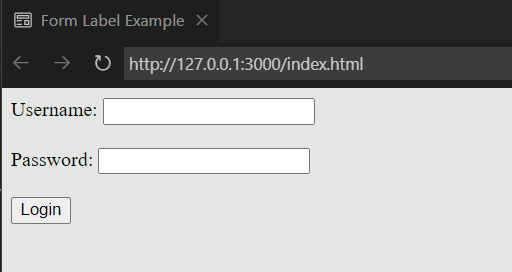
6. Best Practices
- Use Meaningful Names: Choose
idvalues that describe the purpose of the element (e.g.,header,main-content,submit-button). - Avoid Overusing
id: Useidfor unique elements. For styling multiple elements, use theclassattribute instead. - Keep It Simple: Avoid using special characters or complex names for
idvalues. - Test for Uniqueness: Ensure that no two elements share the same
idvalue.
7. Common Mistakes
- Duplicate
idValues: Using the sameidfor multiple elements can cause unexpected behavior in CSS and JavaScript. - Invalid Characters: Using spaces or special characters (e.g.,
#,@,!) inidvalues. - Overusing
id: Usingidfor elements that do not require unique identification.
Conclusion
The id attribute is a powerful tool in HTML for uniquely identifying elements. It is essential for:
- Styling specific elements with CSS.
- Manipulating elements with JavaScript.
- Creating anchor links and improving accessibility.
By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively use the id attribute to enhance the structure, functionality, and usability of your web pages.
