CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to style and format text on web pages. It provides a wide range of properties to control the appearance of text, including font, size, color, alignment, spacing, and more. Below is a comprehensive overview of CSS Text properties and their usage:
1. Font Properties of CSS Text
Font properties control the appearance of the text, including the font family, size, weight, and style.
a. font-family
Specifies the font to be used for the text. You can provide a list of fonts as fallbacks in case the primary font is not available.
p {
font-family: "Arial", "Helvetica", sans-serif;
}- Explanation: The browser will first try to use Arial. If Arial is not available, it will use Helvetica. If neither is available, it will use a generic sans-serif font.
b. font-size
Sets the size of the text. You can use absolute units (e.g., px) or relative units (e.g., em, rem, %).
p {
font-size: 16px; /* Absolute unit */
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em; /* Relative to the parent element */
}- Explanation: em is relative to the font size of the parent element, while
remis relative to the root element (<html>).
c. font-weight
Controls the thickness of the text. Common values include normal, bold, bolder, lighter, or numeric values like 100 to 900.
p {<br> font-weight: bold; /* or 700 */<br>}- Explanation: Numeric values range from
100(thin) to900(thick), with400being normal and700being bold.
d. font-style
Sets the style of the text, such as italic or oblique.
p {
font-style: italic;
}e. font-variant
Used for small-caps or normal text.
p {
font-variant: small-caps;
}- Explanation: Small-caps displays lowercase letters as smaller uppercase letters.
f. line-height
Sets the height of a line of text. It can be a unitless value, percentage, or fixed value.
p {
line-height: 1.5; /* 1.5 times the font size */
}- Explanation: A unitless value (e.g.,
1.5) is relative to the font size, while a fixed value (e.g.,24px) is absolute.
2. Text Color
Sets the color of the text. You can use color names, hex codes, RGB, or HSL values.
p {
color: #ff5733; /* Hex color */
}
h1 {
color: rgb(255, 87, 51); /* RGB color */
}3. Text Alignment
a. text-align
Aligns text horizontally within its container. Values include left, right, center, and justify.
p {
text-align: center;
}- Explanation: justify stretches the text to fill the width of the container.
b. vertical-align
Aligns text vertically within its container. Commonly used for inline or table-cell elements.
img {
vertical-align: middle; /* Aligns image with text */
}4. Text Decoration
Adds decorations like underline, overline, line-through, or none.
a {
text-decoration: none; /* Removes underline from links */
}
p {
text-decoration: underline wavy red; /* Wavy red underline */
}5. Text Transformation
Transforms text to uppercase, lowercase, or capitalize.
p {
text-transform: uppercase; /* Converts text to uppercase */
}6. Text Spacing
a. letter-spacing
Controls the space between characters.
p {
letter-spacing: 2px; /* Adds 2px space between characters */
}b. word-spacing
Controls the space between words.
p {
word-spacing: 5px; /* Adds 5px space between words */
}c. text-indent
Indents the first line of text.
p {<br> text-indent: 20px; /* Indents the first line by 20px */<br>}7. Text Shadow
Adds a shadow to text. The syntax is:
text-shadow: horizontal-offset vertical-offset blur-radius color;Example:
h1 {
text-shadow: 2px 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5); /* Adds a shadow */
}8. White Space and Wrapping
a. white-space
Controls how white space inside an element is handled.
p {
white-space: nowrap; /* Prevents text from wrapping */
}b. word-wrap / overflow-wrap
Allows long words to break and wrap onto the next line.
p {
word-wrap: break-word; /* Breaks long words */
}c. text-overflow
Specifies how overflowed text should be displayed (e.g., ellipsis).
p {
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis; /* Displays ... for overflowed text */
}9. Direction and Writing Mode
a. direction
Sets the text direction (e.g., left-to-right or right-to-left).
p {
direction: rtl; /* Right-to-left */
}b. writing-mode
Defines whether text is written horizontally or vertically.
p {
writing-mode: vertical-rl; /* Vertical text */
}10. Hyphenation
Controls hyphenation of words.
p {
hyphens: auto; /* Automatically hyphenates words */
}11. Text Selection Styling
::selection
Styles the text when it is selected by the user.
::selection {
background-color: yellow;
color: black;
}12. Advanced Text Effects
background-clip: text
Clips the background to the text, creating a gradient or image text effect.
h1 {
background: linear-gradient(90deg, red, blue);
-webkit-background-clip: text;
color: transparent;
}13. Best Practices
- Use Web-Safe Fonts: Always include fallback fonts in
font-family. - Relative Units: Use
em,rem, or%forfont-sizeto ensure scalability. - Readability: Avoid excessive use of
text-transformandtext-decoration. - Cross-Browser Testing: Test text rendering across different browsers and devices.
By mastering these CSS text properties, you can create visually appealing and readable text for your web projects.
14. HTML + CSS Code Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Text Example</title>
<style>
/* General Styles */
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
color: #333;
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
}
/* Heading Styles */
h1 {
font-family: 'Georgia', serif;
font-size: 2.5rem;
font-weight: bold;
color: #2c3e50;
text-align: center;
text-transform: uppercase;
letter-spacing: 2px;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
/* Paragraph Styles */
p {
font-size: 1.1rem;
line-height: 1.6;
text-align: justify;
text-indent: 20px;
word-spacing: 2px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
/* Link Styles */
a {
color: #e74c3c;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
border-bottom: 2px solid #e74c3c;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
a:hover {
color: #c0392b;
border-bottom-color: #c0392b;
}
/* Text Selection Styles */
::selection {
background-color: #3498db;
color: white;
}
/* Advanced Text Effect */
.fancy-text {
font-size: 2rem;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #e74c3c, #3498db);
-webkit-background-clip: text;
background-clip: text;
color: transparent;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
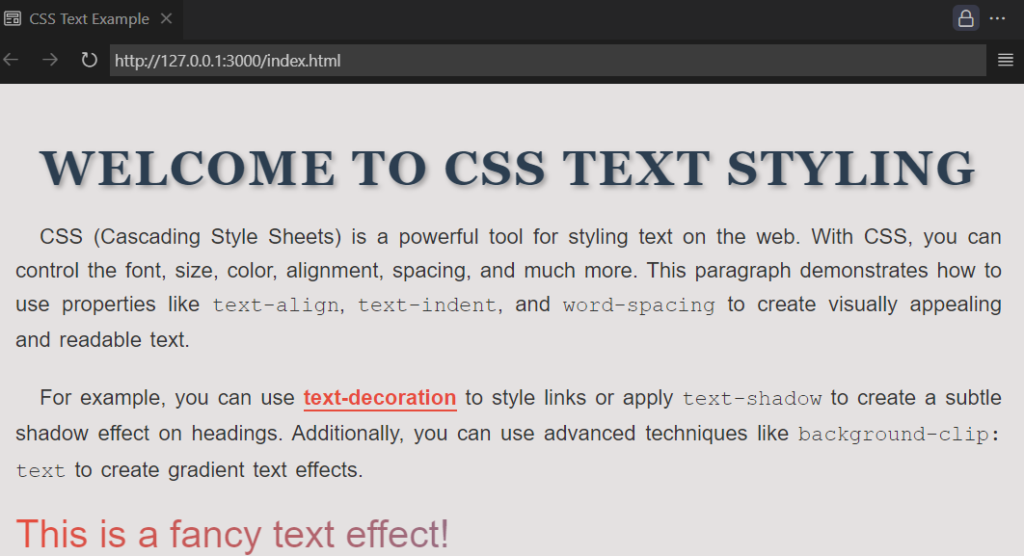
<h1>Welcome to CSS Text Styling</h1>
<p>
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a powerful tool for styling text on the web. With CSS, you can control the font, size, color, alignment, spacing, and much more. This paragraph demonstrates how to use properties like <code>text-align</code>, <code>text-indent</code>, and <code>word-spacing</code> to create visually appealing and readable text.
</p>
<p>
For example, you can use <a href="#">text-decoration</a> to style links or apply <code>text-shadow</code> to create a subtle shadow effect on headings. Additionally, you can use advanced techniques like <code>background-clip: text</code> to create gradient text effects.
</p>
<div class="fancy-text">This is a fancy text effect!</div>
</body>
</html>output: