CSS Margins are used to create space around elements, outside of any defined borders. Margins do not affect the element’s size but influence spacing between elements.
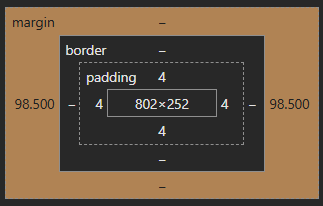
1. Basic Margin Example
This example demonstrates how margins create space around a <div>.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Margins Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
margin: 20px; /* 20px margin on all sides */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">Box with Margin</div>
</body>
</html>Explanation
- The <div> has width: 200px and height: 100px.
- margin: 20px; adds 20px of space on all four sides.
2. Different Margin Values for Each Side
Margins can be specified for individual sides: margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom, and margin-left.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Different Margins</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
margin-left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">Different Margins</div>
</body>
</html>Explanation
- margin-top: 10px; → 10px space above.
- margin-right: 20px; → 20px space to the right.
- margin-bottom: 30px; → 30px space below.
- margin-left: 40px; → 40px space to the left.
3. Margin Shorthand Notation
Instead of writing margins separately, you can use shorthand notation.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Margin Shorthand</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px; /* Top Right Bottom Left */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">Shorthand Margin</div>
</body>
</html>Shorthand Rules
- margin: 10px; → All sides get 10px.
- margin: 10px 20px; → Top & bottom: 10px, Left & right: 20px.
- margin: 10px 20px 30px; → Top: 10px, Left & right: 20px, Bottom: 30px.
- margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px; → Top: 10px, Right: 20px, Bottom: 30px, Left: 40px.
4. Auto Margin for Centering Elements
margin: auto; is commonly used to horizontally center block elements.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Centering with Margin</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
margin: 50px auto; /* Centers horizontally */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">Centered Box</div>
</body>
</html>Explanation
- margin: 50px auto; → Top & bottom: 50px, Left & right: auto (centers the block).
5. Negative Margins
Negative margins reduce the space instead of adding it.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Negative Margins</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightpink;
margin-top: -20px; /* Moves element upwards */
margin-left: -30px; /* Moves element left */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">Negative Margins</div>
</body>
</html>Explanation
- margin-top: -20px; → Moves the element up by 20px.
- margin-left: -30px; → Moves the element left by 30px.
6. Using inherit for Margins
The inherit value makes an element inherit the margin from its parent.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Inherit Margin</title>
<style>
.parent {
margin: 30px;
}
.child {
background-color: lightyellow;
margin: inherit; /* Inherits 30px margin from parent */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="child">Inherited Margin</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Explanation
- The .parent div has margin: 30px;.
- The .child div inherits this value using margin: inherit;.
Conclusion
CSS margins are essential for controlling the spacing between elements on a webpage. They help in structuring layouts, improving readability, and ensuring proper alignment.
Key Takeaways:
- Margins create space outside an element’s border.
- Margins can be set individually (margin-top, margin-right, etc.) or using shorthand notation.
- margin: auto; is useful for centering block elements.
- Negative margins move elements closer together by reducing space.
- The
inheritvalue allows elements to adopt the margin of their parent.
