The CSS Box Model is a core concept in web development that determines how elements are structured and how their dimensions (width, height, padding, border, and margin) interact with each other. Understanding it is essential for controlling element layouts and spacing.
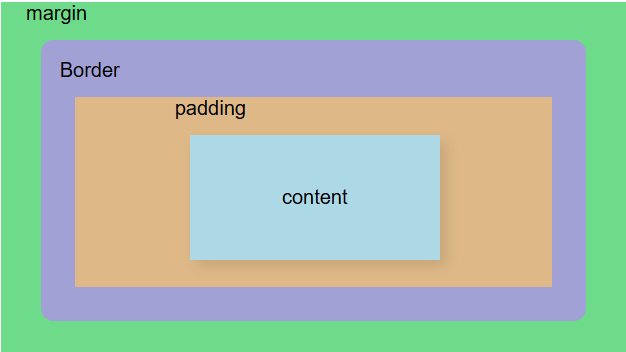
1. Components of the Box Model
Every HTML element is represented as a rectangular box, which consists of the following parts:
a. Content
- The area where text, images, or other content is displayed.
- Its dimensions are defined by width and height properties.
- Default behavior: If no explicit width/height is set, the content area will expand based on its content.
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}Note: The width and height set here only affect the content area unless modified by box-sizing.
b. Padding
- Space between the content and the border.
- It increases the element’s size inside the border.
- Can be set individually for each side (padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, padding-left) or all at once using padding.
.box {
padding: 20px; /* Applies 20px padding on all sides */
}OR
.box {
padding: 10px 20px 15px 5px; /* Top, Right, Bottom, Left */
}Effect: Expands the inner space of the element, pushing content inward.
c. Border
- A visual edge around the content and padding.
- Affects the overall size of the element.
- Can have different styles (solid, dashed, double, none, etc.), thickness, and colors.
.box {
border: 5px solid black; /* 5px thick, solid black border */
}OR
.box {
border-top: 3px dashed red; /* Dashed red border only on top */
}Effect: Adds a visible frame to the element.
d. Margin
- Space outside the border that separates elements from each other.
- Like padding, margins can be set for each side individually or all at once.
.box {
margin: 15px; /* Adds 15px margin on all sides */
}OR
.box {
margin: 10px 20px 5px 0; /* Top, Right, Bottom, Left */
}Effect: Controls spacing between elements.
2. Box Model Calculation
The total width and height of an element are not just the specified width and height; they include padding, border, and margin.
Formula for Total Element Size:
Total Width = content width + left padding + right padding + left border + right border + left margin + right margin
Total Height = content height + top padding + bottom padding + top border + bottom border + top margin + bottom margin🔹 Example Calculation:
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
padding: 20px;
border: 5px solid black;
margin: 10px;
}- Total Width = 200px + (20px + 20px) + (5px + 5px) + (10px + 10px) = 270px
- Total Height = 100px + (20px + 20px) + (5px + 5px) + (10px + 10px) = 170px
Issue: If an element has fixed width (200px), adding padding/border increases the actual size, potentially breaking layouts.
3. The box-sizing Property
By default, width and height only apply to the content, but you can change this behavior using box-sizing.
a. Default Behavior (content-box)
- The specified width/height applies only to the content.
- Padding and border increase the total size.
.box {
width: 200px;
padding: 20px;
border: 5px solid black;
box-sizing: content-box; /* Default behavior */
}Problem: The actual width will be 270px, not 200px.
b. border-box Mode (Recommended)
- Width and height include padding and border.
- The total size remains what you set.
.box {
width: 200px;
padding: 20px;
border: 5px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box; /* Keeps the total width at 200px */
}Solution: The element stays 200px wide, and the padding/border adjust inside.
4. Margin Collapse
When vertical margins of two elements meet, they collapse instead of adding up.
.box1 {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.box2 {
margin-top: 30px;
}Instead of 50px (20px + 30px), the margin will be 30px (the larger value).
5. Visual Representation of the Box Model
+--------------------------------------------------+
| Margin (outside space, invisible) |
| +--------------------------------------------+ |
| | Border (visible edge of the box) | |
| | +-----------------------------------+| | |
| | | Padding (inner space) | | |
| | | +-------------------------------+ | | |
| | | | Content (text, images, etc.) | | | |
| | | +-------------------------------+ | | |
| | +------------------------------------+ | |
| +--------------------------------------------+ |
+--------------------------------------------------+6. Practical Use Cases
Creating a Button with Spacing:
.button {
padding: 10px 20px;
border: 2px solid black;
margin: 5px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}Ensuring Consistent Layouts:
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}Applying box-sizing: border-box; globally prevents unexpected layout shifts.
7. Summary
| Property | Affects | Description |
|---|---|---|
| width / height | Content | Sets size of content area. |
| padding | Inside | Adds space inside the border. |
| border | Edge | Adds a frame around the content. |
| margin | Outside | Adds space between elements. |
| box-sizing | All | Controls how width/height is calculated. |
Key Takeaways:
- Default behavior (content-box) makes elements bigger than expected.
- box-sizing: border-box; keeps elements the size you set.
- Padding pushes content inward, margin pushes elements apart.
- Margins can collapse, but padding and borders do not.
